Causes, symptoms, and management for head lice
Head lice, a common parasitic infestation, can be a source of discomfort and concern for both children and adults. These tiny insects live on the scalp and feed on blood, causing itching and irritation. While head lice infestations are not a sign of poor hygiene, they can spread easily through close contact. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for head lice is essential in effectively managing and preventing their spread.
Causes of Head Lice
Head lice infestations are primarily caused by the transmission of the louse from one person to another. The most common modes of transmission include:
Direct contact
Head-to-head contact with an infested person is the most common way head lice are spread. This often occurs during playtime, sleepovers, or other activities that involve close physical contact.
Sharing personal items
Lice can also spread when individuals share personal items such as combs, brushes, hats, scarves, helmets, or hair accessories with someone who has an infestation.
Indirect contact
Although less common, head lice can be transmitted through indirect contact with objects, such as furniture or bedding, that have come into contact with someone with lice.
Symptoms of Head Lice Infestation
Itching
Intense itching of the scalp is the most common symptom of head lice infestation. The itching is caused by the lice biting the scalp and the body’s reaction to their saliva.
Visible lice and nits
Adult lice are tiny, about the size of a sesame seed, and have a tan or grayish color. Nits, or lice eggs, are tiny white or yellowish oval-shaped eggs attached to the hair shaft near the scalp.
Irritated scalp
The presence of head lice and their bites can lead to an irritated and red scalp, which may result in secondary bacterial infections if scratched excessively.
Restlessness
Children may exhibit signs of restlessness or difficulty sleeping due to the discomfort caused by head lice.
Treatment Options for Head Lice
Over-the-Counter (OTC) solutions
There are various OTC shampoos, lotions, and sprays specifically formulated to kill lice. These products often contain pyrethrins or permethrin, which are effective in eliminating the pests.
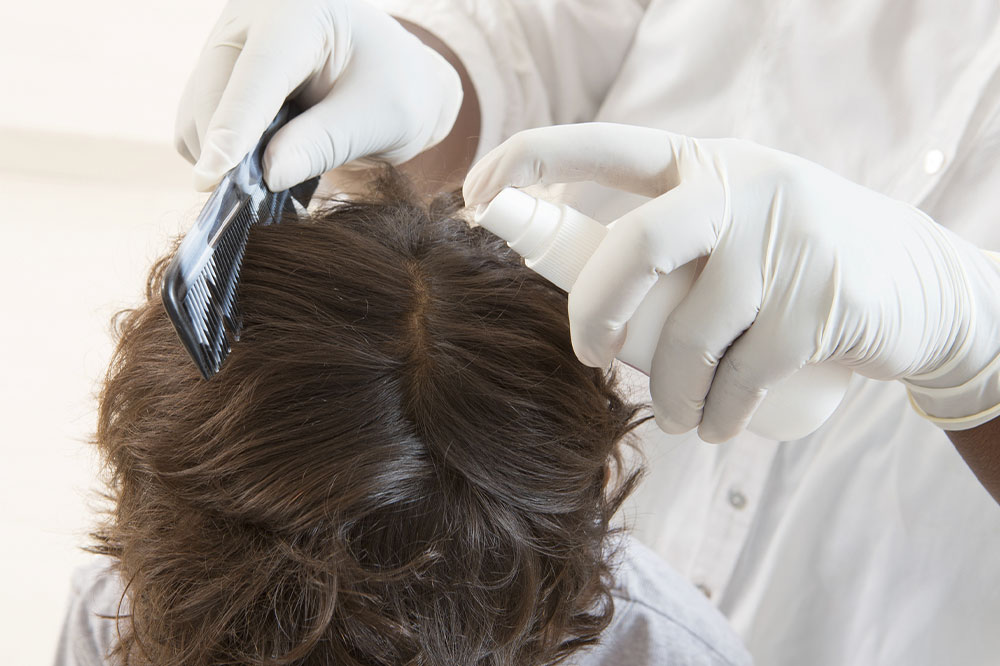
Manual removal
Manual removal of lice and nits with a fine-toothed nit comb can be an effective complement to prescription treatment. Regular combing can help remove remaining lice and prevent re-infestation.
Environmental cleaning
To prevent re-infestation, it is essential to wash and dry all clothing, bedding, and personal items that may have come into contact with an infested person in hot water and high heat.
Avoiding close contact
Minimizing close head-to-head contact with others can help prevent the spread of head lice.
Dealing with head lice requires prompt and appropriate action to prevent their spread and alleviate discomfort. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for head lice is crucial in effectively managing and eradicating infestations. Quick detection and early treatment with OTC solutions, along with thorough manual removal and environmental cleaning, can help eliminate the condition altogether. Moreover, promoting awareness about head lice transmission and practicing good hygiene, such as avoiding the sharing of personal items, can contribute to preventing future infestations. By adopting preventive measures and taking swift action when head lice are detected, individuals can effectively address this common and manageable concern, ensuring a comfortable and lice-free scalp for themselves and their loved ones.